- HubPages»
- Education and Science»
- History & Archaeology»
- History of the Middle East
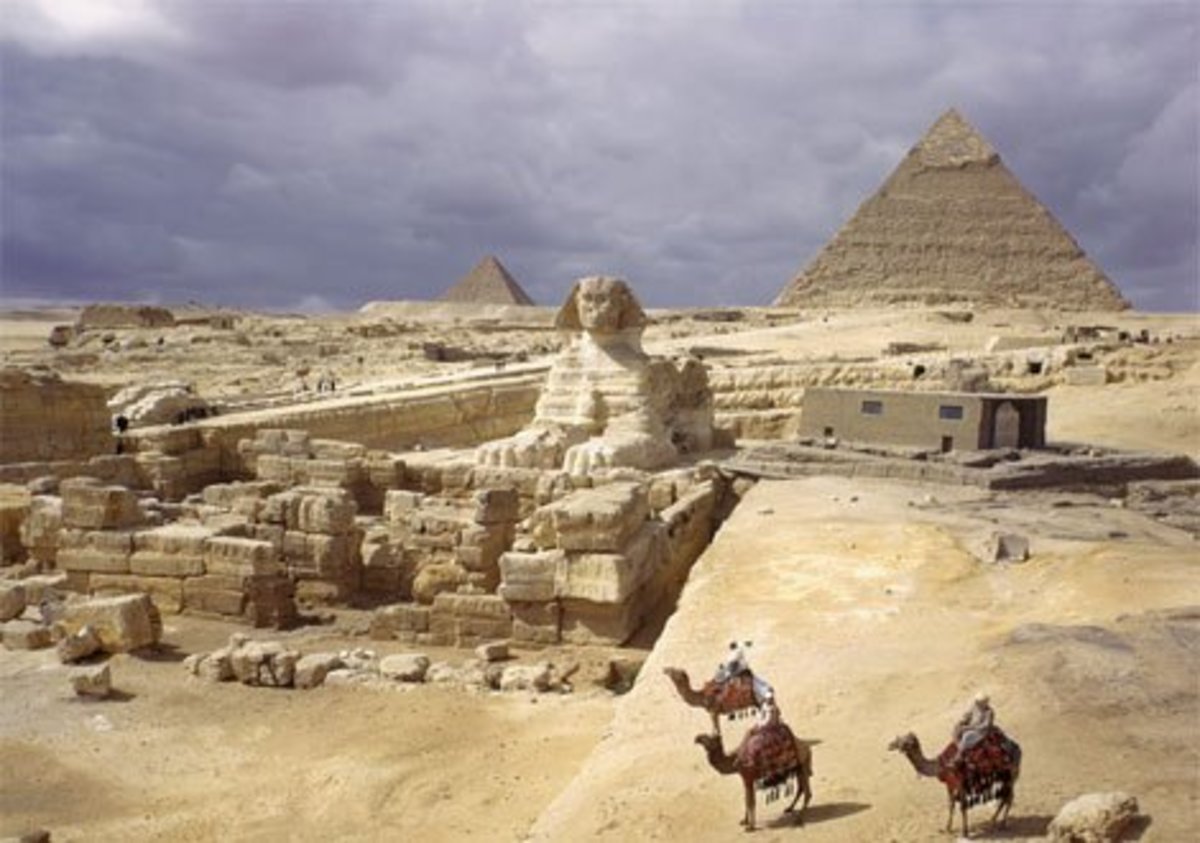
The Pyramids
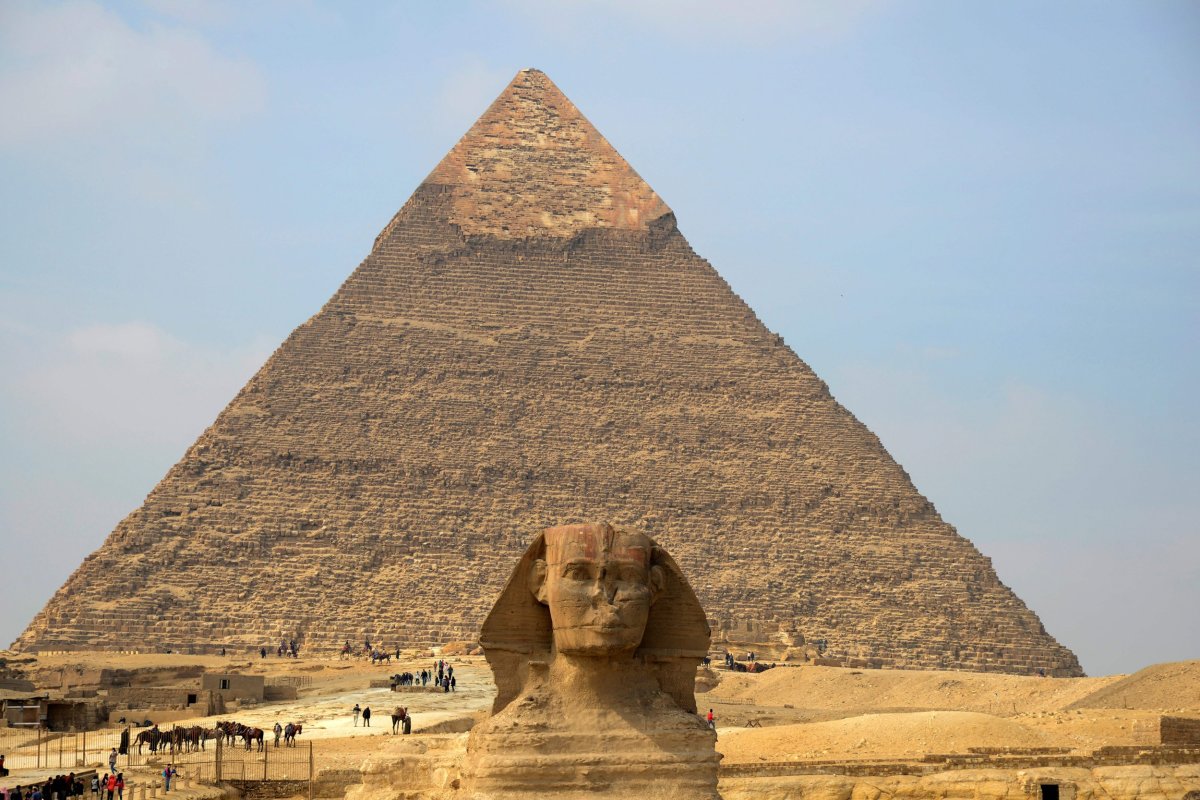
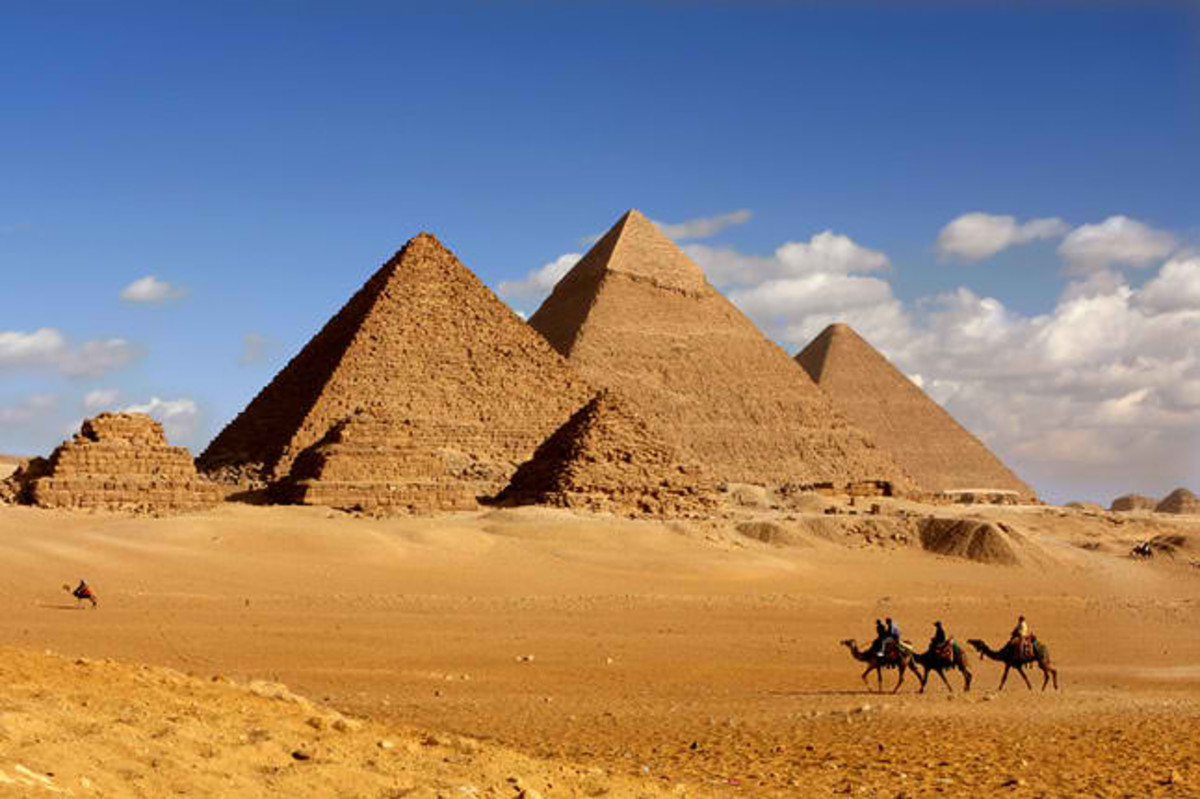
Pyramids are old stone buildings with a square base. These pyramids were built by ancient Egyptian's to serve as tombs for their kings and queens especially during 2614-2181 BC. The most famous are the pyramids in Giza. Khofo, Khafraa, Monkara
They are found in the south west of Egypt's capital, Cairo, The biggest and the oldest is the Khofo pyramid. Archaeologist are still digging for more pyramids along the Nile
Who built the great Pyramid?
The pyramids according to common perception were built with the begrudging help of armies of slaves, by the ancient pharaohs of Egypt as tombs to preserve their royal bodies. Pyramids were meant to be monuments to the pharaoh's greatness, filled with great treasures for the afterlife. To construct these massive shrines, the pharaohs followed the architectural design of the oldest and largest pyramid of all "The Great Pyramid of Giza". But the great pyramid itself contains no pharaohs' body, no treasures.

Facts about the Pyramids of Egypt
- The last wonder of the world
- Thirty times larger than the empire state building, the pyramids are so large that they can be seen from the moon.
- Its base covers 13.6 acres, each side being greater than five acres in area
- The oldest structure in existence, having been started 4,617 years ago, it is the sole remnant of the Seven Wonders of the World.
Journey to the centre of the Earth
- Only a solid stone mountain could endure the pyramids immense weight and indeed, flat solid granite mountain happens to be located just beneath the surface of the ground directly under the pyramid.
- It is built to face true north.
- The pyramid is located at the exact centre of the mass. That is its east-west axis corresponds to the longest land parallel across the earth, passing though Africa, Asia and America.

Construction unequaled by modern technology
- Like 20th century bridge designs, the pyramid's cornerstone has balls and sockets built into them. Several football fields long, the pyramid is subject to expansion and contraction movements from heat and cold as well as earthquake, settling and other such phenomena.
- After 4,600 years its structure would have been significantly damaged without such construction
- Pyramid was made of a beautifully bright, protective layer of polished stone. These outer casing stones are missing today because about 600 years ago they were taken by the Arabs. This protective covering was made up of 100 inch thick, 20- ton block of hard, white limestone, similar to marble but superior in hardness and in durability against the elements.
- Amazingly the outside surface stones are cut within 0.01 inch of perfectly straight and at nearly perfect right angles for all six sides and they were placed together with an intentional gap between them of 0.02 inch. Modern technology cannot place such 20 ton stones with great accuracy than those in the pyramid.
The cosmic yardstick
The great pyramid is one of the most comprehensively surveyed buildings in the world. Scientists over the centuries have taken thousands of great measurements in their quest to find out more about its mysteries.
- Each of the pyramids' four walls, when measured as a straight line is 9,131 inches for a total of 36,524 inches. At first glance, this number may not seem significant, but move the decimal point over and you get 365.24. Modern science has shown us that the exact length of the solar year is 365.24.
- The average height of land above sea level (Miami being low and the Himalayas being high), as can be measured only by modern day satellites and computers, happens to be 5449 inches; this is the exact height of the pyramid.
- All four sides of the pyramid are very slightly and evenly bowed in or concave this effect cannot be detected by looking at the pyramid from the ground. It was discovered around 1940 by a pilot taking aerial photos to check certain measurements. As measured by today's laser instrument all of these perfectly cut and intentionally bowed stone blocks duplicate exactly the curvature of the earth. The radius of this bow is equal to the radius of the earth.

Great architecture
Various possible methods of constructing pyramids:
- Counter weight mechanism - Back in ancient Egypt, a device called a shadoof was commonly used to move water. A shadoof is a long pole, weighted at one end, perhaps with a stone, and the vessel on the other end, using water to irrigate the land. They pulled down the vessel, filled it under the water, and easily lifted it up by the counter weight. These water lifting machines showed that the Egyptians knew something about weights, fulcrum, and balance long before they built the pyramids. Maybe they have used this mechanism to carry huge stone to certain required height.
- Round logs platform method - Perhaps the Egyptians rolled the stones by placing them on platforms and used round logs under the platform to push the stones along. However, the difficulty of getting the five-ton block off and on the platform exists.
- Windlass mechanism -At the time the pyramids were built, basic devices to pull heavy stones such as windlass were very much in use. The windlass is a wheel and axle machine where the axle is fastened to the wheel. On both sides of the axle are large wheels, poles, much larger than the axle. By winding a rope around the axle and turning the wheel a mechanical advantage equal to the ratio of the diameter of the wheel to that of the axle is realized. By putting the stone on a skid and using the windlass, six men could move the stone across the surface much easier by putting the windlass on the level of the pyramid they are working on, the six men could hoist stone up the side of the pyramid on a narrow ramp. To lift a five ton stone using a shadoof, the counter weight would have to weigh almost as much as the stone to be lifted.
- Usage of ramps built on inclined planes - A major problem facing the builder of Ancient Egyptian pyramids was that of getting the large stone blocks to the height they required. The ramps were built on inclined planes of mud brick and rubble. They then dragged the blocks on sledges to the needed height. As the pyramid grew taller, the ramp had to be extended in length, and its base widened, else it would collapse. It is likely that for the construction of each pyramid, several ramps were probably used.
- Arrangement of ramps -The arrangement of the ramps used for building is much disputed. Assuming that the step pyramid was built before the outer structure, and then the packing blocks were laid on top, the ramps could have run from one step to another rather than approaching the pyramid face at right angles.
- Pi method - Some of the pyramids indicate an accurate understanding of Pi, but the mathematical knowledge of the Egyptians did not include the ability to arrive at this by calculation. It is possible that this could have been arrived at ‘accidentally' through a means such as counting the revolution of a drum.
- Series of buttress walls surrounding a central core -This internal construction of most true pyramids consists of a series of buttress surrounding a central core. The walls decrease in height from the centre outwards. In other words, the core of the true pyramid is essentially a step pyramid. The internal arrangement added stability to the structure. Packing blocks filled the steps formed by the faces of the outermost buttress walls and casting blocks (often Limestone) completed the structure of the true pyramid.
- Architects and builders method - Architects and builders used a different form of construction in the pyramids of the 12th and 13th Dynasties. Mainly because economically it was suitable for relatively modest structures in inferior materials. Solid stone ran from the centre, and shorter cross walls form a series of chambers filled with stone blocks, ruble or mud bricks. An outer casting was usually added, and although quite effective in the short term, it did not even come close to the earlier construction methods. Pyramids, which were built with this structural design, are quite dilapidated and worn. Till now it's a mystery how ancient Egyptians lifted a 20 to 50 ton stone and placed it with such great accuracy. Let's hope someone solves the mystery in the future.
- Seven Wonders Of The Ancient World
Although most people know that a list exists of the Seven World Wonders, only few can name them. The list of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World was originally compiled around the second century BC. The... - Mythical Gods And Creatures
In Greek mythology living beings come under two categories, that is, they are either gods and heroes, or creatures. Gods have most characteristics of humans, but along with this they also have supernatural... - Some Facts About The Roman Empire
According to legend, Rome was a settlement of a mixture of native Latins and the survivors of the Trojan War who were brought to Italy in the 12th century. On a date corresponding to April 21, 753BC, the city...